US GDP
May 31, 2024What is going to be the impact of AI on GDP in the United States? A model has been developed and a forecast has been made.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, artificial intelligence (AI) stands out as a transformative force with the potential to reshape economies worldwide. As businesses and governments increasingly adopt AI technologies, understanding how AI will influence Gross Domestic Product (GDP) becomes crucial. In this blog post, we will explore the multifaceted impact of AI on GDP, delving into its potential benefits and challenges.
Enhancing Productivity and Efficiency
One of the most significant ways AI can influence GDP is through enhancing productivity and efficiency. AI-powered automation and machine learning algorithms can streamline operations, reduce errors, and optimize processes across various industries. For example, in manufacturing, AI-driven robots can operate around the clock without fatigue, significantly increasing output and reducing production costs. These productivity gains translate directly into higher economic output, boosting GDP.
Driving Innovation and Creating New Markets
AI is a catalyst for innovation, enabling the development of new products and services that can create entirely new markets. Companies leveraging AI for research and development are achieving breakthroughs that were previously unattainable, from advanced medical treatments to cutting-edge technologies. These innovations stimulate economic activity and generate substantial revenue, contributing positively to GDP. The rise of AI-driven industries, such as autonomous vehicles and personalized healthcare, exemplifies this transformative potential.
Reducing Costs and Increasing Competitiveness
Another critical impact of AI on GDP is its ability to reduce operational costs. By automating routine tasks and improving efficiency, AI helps businesses lower their operating expenses. These savings can be passed on to consumers through lower prices, increasing demand, or reinvested into further innovation and expansion. For instance, AI-driven predictive maintenance in industries like aviation and logistics can prevent costly downtime and extend the lifespan of equipment, enhancing overall competitiveness and economic growth.
Boosting Consumer Spending and Experience
AI’s influence extends to the demand side of the economy as well. By enhancing consumer experiences, AI drives spending and boosts economic activity. Personalized recommendations, improved customer service, and faster delivery times facilitated by AI make shopping more convenient and enjoyable, encouraging consumers to spend more. Additionally, as AI reduces costs in essential sectors like healthcare and education, consumers may have more disposable income to spend on other goods and services, further driving GDP growth.
Addressing Job Displacement and Income Inequality
While AI offers numerous economic benefits, it also presents challenges that could negatively impact GDP if not managed properly. One significant concern is job displacement. As AI and automation advance, certain jobs may become obsolete, leading to higher unemployment rates. This displacement can reduce overall consumer spending and economic activity. To mitigate this, it is crucial to implement policies that support retraining and reskilling programs, helping workers transition to new roles in the AI-driven economy.
Promoting Inclusive Growth
Income inequality is another potential issue. The economic benefits of AI might be concentrated among those who own and control the technology, leading to wider disparities. If the majority of the population does not share in the economic gains, aggregate demand could suffer, hindering GDP growth. Addressing this requires inclusive growth policies that ensure the widespread distribution of AI’s benefits. Measures such as progressive taxation, social safety nets, and equitable access to education and technology are essential.
Managing Economic Disruption
The transition to an AI-driven economy can also cause temporary economic disruption. As industries transform, there may be periods of instability and adjustment, which could temporarily depress economic growth. Businesses and workers may need time to adapt to new technologies and market conditions. Effective management of this transition through supportive policies and infrastructure investments is crucial to minimizing negative impacts on GDP.
Modeling the Impact of AI on GDP
Creating a mathematical model to show the numeric relationship between AI acceptance and GDP involves identifying key variables and establishing their relationships. Here is our first generation model to demonstrate this concept:
Variables:
- GDP (Y): Gross Domestic Product.
- AI Acceptance (A): Level of AI integration and usage within the economy.
- Productivity (P): Productivity gains from AI.
- Innovation (I): Innovation and new products/services driven by AI.
- Cost Reduction (C): Operational cost savings due to AI.
- Consumer Spending (S): Increase in consumer spending due to AI.
- Job Displacement (D): Negative impact on GDP from job displacement.
- Income Inequality (Q): Negative impact on GDP from income inequality.
Model structure
Let’s consider that GDP (Y) is a function of AI Acceptance (A), where AI Acceptance influences Productivity (P), Innovation (I), Cost Reduction (C), Consumer Spending (S), Job Displacement (D), and Income Inequality (Q)
\[ \begin{aligned} Y=α+β_1P+β_2I+β_3C+β_4S−β_5D−β_6Q \end{aligned} \]Where \(α\) is the constant term, and \(β_1, β_2, β_3, β_4, β_5, β_6\) are the coefficients representing the impact of each variable on GDP.
Each of these factors (P, I, C, S, D, Q) can be modeled as functions of AI Acceptance (A):
\[ P=γ_1A \]etc.
Leading to the equation:
\[ Y=α+β_1γ_1A+β_2γ_2A+β_3γ_3A+β_4γ_4A−β_5γ_5A−β_6γ_6A \]or
\[Y=α+A(β_1γ_1+β_2γ_2+β_3γ_3+β_4γ_4−β_5γ_5−β_6γ_6)\]Coefficients and resulting model
The following values are proposed for the $β$ coefficients in the model:
\[β_1(Productivity)=0.3\] \[β_2(Innovation)=0.25\] \[β_3(Cost Reduction)=0.2\] \[β_4(Consumer Spending)=0.35\] \[β_5(Job Displacement)=0.08\] \[β_6(Income Inequality)=0.04\]And for the \(γ\) coefficients:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| \(γ_1=6\) | \(γ_1\) is effect of AI acceptance on productivity |
| \(γ_2=5\) | \(γ_2\) is effect of AI acceptance on innovation |
| \(γ_3=4\) | \(γ_3\) is effect of AI acceptance on cost reduction |
| \(γ_4=7\) | \(γ_4\) is effect of AI acceptance on consumer spending |
| \(γ_5=2.5\) | \(γ_5\) is effect of AI acceptance on job displacement |
| \(γ_6=1.5\) | \(γ_6\) is effect of AI acceptance on income inequality |
The model can then be simplified to:
\[Y=α+δA\]Where δ=12
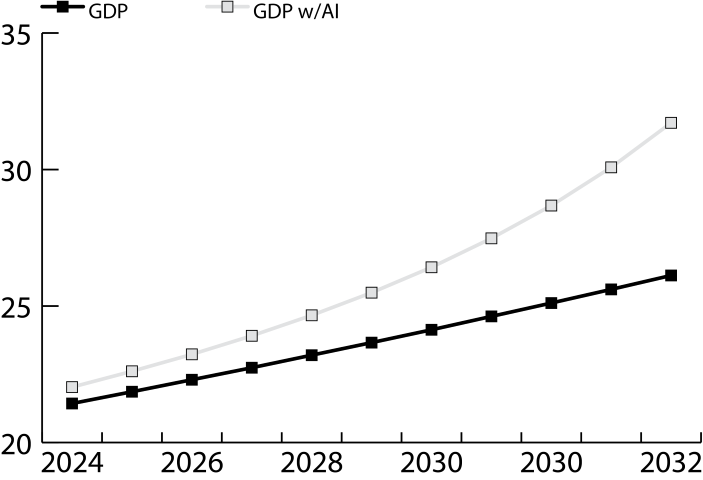
Baseline - 2024
Current estimated US GDP is $21.43 trillion
Y=21,430,000+12A
Current AI acceptance is estimated at 5% (A=50,000), resulting in a contribution of about $0.5 to the US GDP.
Forecast - 2030
As an assumption a non-AI contributed GDP growth of 2% per year is assumed. This results in a GDP of $24.1 trillion in 2030.
By 2030, the model predicts that AI acceptance will have increased to 20% (A=200,000) and representing a contribution of $6T to the US GDP. This would result in a 2030 US GDP of $26.4 trillion.
10 year forecast - 2034
By 2030, the model predicts that AI acceptance will have increased to 50% (A=500,000) and representing a contribution of $5.5T to the US GDP. This would result in a 2034 US GDP of $31.7 trillion.