Adoption rate of humanoid robots
June 4, 2024Humanoid robots have transitioned from the realm of science fiction into a burgeoning field of technological innovation. These robots, designed to resemble and mimic human actions, have seen significant advancements in recent years, becoming increasingly integrated into various sectors of society. This article explores the technological developments, applications, challenges, and adoption rates of humanoid robots, painting a comprehensive picture of their current status and future prospects.
Humanoid robots represent a significant technological leap with the potential to transform various sectors. While there are challenges to overcome, the advancements in technology, combined with the growing interest and investment in robotics, indicate a bright future. As costs decrease and capabilities increase, humanoid robots are likely to become an integral part of our everyday lives, enhancing productivity, improving quality of life, and opening new frontiers of innovation.
Technological Developments in Humanoid Robots
| Development Area | Key Technologies | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Design | Actuators, Control Algorithms | Advanced actuators and control algorithms for precise and coordinated movement. |
| Locomotion | Bipedal Walking, Hybrid Systems | Systems enabling robots to walk, run, and navigate complex terrains. |
| Artificial Intelligence | Machine Learning, Deep Learning | AI algorithms that allow robots to learn, adapt, and make decisions. |
| Sensory Systems | Cameras, LIDAR, Tactile Sensors | Sensors for vision, touch, and environment mapping. |
| Energy Efficiency | Regenerative Braking, High-Capacity Batteries | Technologies to optimize power consumption and extend operational time. |
| Human-Robot Interaction | Natural Language Processing, Gesture Recognition | Technologies to improve communication and interaction with humans. |
| Autonomous Navigation | SLAM, Real-time Path Planning | Systems for self-navigation and obstacle avoidance in dynamic environments. |
| Materials and Durability | Advanced Composites, Lightweight Alloys | Use of durable, lightweight materials for building robots. |
1. Mechanical Design and Locomotion
One of the fundamental aspects of humanoid robots is their mechanical design, which enables them to move and interact with their environment. Early humanoid robots were limited in their movement capabilities, but recent advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated locomotion systems. Modern humanoid robots can walk, run, climb stairs, and even perform complex maneuvers such as backflips. This progress is largely due to advancements in actuators, which convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, and the development of sophisticated control algorithms that ensure stability and coordination.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) has been a game-changer for humanoid robots. AI enables these robots to process vast amounts of data, learn from experiences, and make decisions in real-time. Machine learning algorithms, particularly deep learning, allow robots to recognize patterns, understand natural language, and even exhibit behaviors that seem intuitive. These capabilities are crucial for tasks that require interaction with humans and adaptation to dynamic environments.
3. Sensory Systems
Sensory systems are another critical component of humanoid robots. These systems include cameras for vision, microphones for hearing, and tactile sensors for touch. Advanced sensory systems enable robots to perceive their environment with high accuracy, facilitating tasks such as object recognition, navigation, and human-robot interaction. The development of 3D vision systems and LIDAR technology has further enhanced the robots’ ability to understand and navigate complex environments.
4. Energy Efficiency and Power Management
Energy efficiency remains a significant challenge for humanoid robots. As these robots become more capable and complex, their energy consumption increases. Researchers are addressing this challenge by developing more efficient power management systems and exploring alternative energy sources. Innovations such as regenerative braking, where energy is recaptured during movement, and the development of high-capacity, lightweight batteries are crucial for extending the operational time of humanoid robots.
Applications of Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots are being deployed in a variety of applications, each leveraging their unique capabilities to solve specific problems.
1. Healthcare
In healthcare, humanoid robots are being used to assist with patient care, rehabilitation, and surgical procedures. They can perform tasks such as lifting patients, delivering medications, and providing companionship to the elderly. Robots like Pepper and NAO are used in therapeutic settings to engage with patients, particularly those with autism or other developmental disorders.
2. Manufacturing and Logistics
Humanoid robots are also making their mark in manufacturing and logistics. They are employed to perform repetitive tasks, handle hazardous materials, and work alongside human workers on assembly lines. In logistics, robots are used for sorting, packaging, and transporting goods within warehouses, improving efficiency and reducing labor costs.
3. Customer Service
In the customer service sector, humanoid robots are deployed as receptionists, guides, and retail assistants. They can greet customers, provide information, and assist with transactions. Robots like SoftBank’s Pepper are already in use in various retail stores, airports, and hotels, enhancing customer experience through their interactive capabilities.
4. Education and Research
Educational institutions and research facilities are using humanoid robots to teach programming, robotics, and AI. These robots provide a hands-on learning experience, helping students understand complex concepts in a more interactive and engaging manner. Additionally, researchers use humanoid robots to study human-robot interaction, biomechanics, and cognitive science.
Challenges in the Adoption of Humanoid Robots
Despite the significant advancements, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of humanoid robots.
1. Cost
One of the primary barriers to the adoption of humanoid robots is their cost. Developing, manufacturing, and maintaining these robots require substantial investment. While costs are gradually decreasing due to advancements in technology and economies of scale, they remain prohibitively high for many potential users, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises.
2. Complexity and Reliability
Humanoid robots are complex systems that require precise engineering and programming. Ensuring their reliability and robustness in diverse and unpredictable environments is a significant challenge. Any malfunction or error can lead to operational failures, which can be costly and potentially dangerous.
3. Ethical and Social Concerns
The integration of humanoid robots into society raises various ethical and social concerns. Issues such as job displacement, privacy, and the ethical implications of autonomous decision-making need to be addressed. There is also the question of how robots should be designed and used to ensure they are accepted and trusted by the public.
4. Regulatory and Legal Frameworks
The rapid advancement of humanoid robot technology has outpaced the development of regulatory and legal frameworks. Clear regulations are needed to ensure the safe and ethical deployment of robots. This includes establishing standards for safety, accountability, and data protection.
Likely Adoption of Humanoid Robots in the Auto Industry
The automotive industry, characterized by its emphasis on precision, efficiency, and innovation, is poised to be a significant adopter of humanoid robots.
The adoption of humanoid robots in the auto industry is likely to grow significantly in the coming years. Their potential to enhance efficiency, improve quality, and reduce costs makes them an attractive option for various applications within the industry. While there are challenges to overcome, the benefits of integrating humanoid robots into the automotive production process are substantial. As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of humanoid robots, transforming the auto industry and setting new standards for innovation and productivity.
Here are several aspects and factors that highlight the likely adoption of humanoid robots in the auto industry:
1. Assembly Line Automation
-
Enhanced Efficiency: Humanoid robots can perform repetitive tasks with high precision and consistency, which is crucial for assembly lines. They can work alongside human workers or entirely automate certain sections of the assembly process, increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
-
Flexibility: Unlike traditional industrial robots that are fixed in place, humanoid robots can navigate around the assembly line and perform various tasks. This flexibility allows them to adapt to changes in production requirements and configurations.
-
Quality Control: Humanoid robots equipped with advanced sensors can conduct real-time inspections, ensuring that every component meets the required quality standards. This helps in identifying defects early in the production process, reducing waste and improving product quality.
2. Maintenance and Inspection
-
Predictive Maintenance: Humanoid robots can be deployed to perform routine inspections and maintenance tasks. Equipped with AI and machine learning algorithms, they can predict potential failures and perform preventive maintenance, minimizing downtime and extending the life of equipment.
-
Hazardous Tasks: In environments that are dangerous for human workers, such as those involving high temperatures or toxic chemicals, humanoid robots can be employed to carry out maintenance and inspection tasks, ensuring worker safety.
3. Supply Chain and Logistics
-
Warehouse Management: Humanoid robots can manage inventory, handle materials, and optimize warehouse operations. Their ability to navigate complex environments and interact with various objects makes them ideal for automating warehouse tasks.
-
Just-in-Time Production: By ensuring that the right components are delivered to the assembly line at the right time, humanoid robots can help implement just-in-time production methods, reducing inventory costs and improving operational efficiency.
4. Customer Interaction and Sales
-
Showroom Assistants: In auto showrooms, humanoid robots can serve as customer assistants, providing information about vehicles, answering questions, and even guiding customers through the purchasing process. This enhances customer experience and frees up human sales representatives to focus on more complex tasks.
-
Test Drives and Demonstrations: Humanoid robots can be programmed to demonstrate vehicle features and conduct virtual test drives, offering customers an interactive and engaging experience.
5. Research and Development
-
Prototyping and Testing: Humanoid robots can assist in the prototyping and testing of new vehicle models. Their ability to simulate human actions and interactions can help engineers and designers understand how real users might interact with new designs.
-
Data Collection: By collecting and analyzing data during testing phases, humanoid robots can provide valuable insights that drive innovation and improve vehicle design and functionality.
Factors Driving Adoption
1. Technological Advancements
-
Improved Robotics Technology: Advances in robotics technology, including AI, machine learning, and sensor technology, make humanoid robots more capable and reliable. This enhances their utility in various aspects of the automotive industry.
-
Integration with IoT and Smart Manufacturing: The integration of humanoid robots with IoT devices and smart manufacturing systems facilitates seamless operations, real-time data collection, and process optimization.
2. Economic Benefits
-
Cost Savings: While the initial investment in humanoid robots can be high, the long-term cost savings in terms of increased productivity, reduced errors, and lower maintenance costs can be substantial.
-
Competitive Advantage: Early adopters of humanoid robots can gain a competitive edge by improving operational efficiency, product quality, and customer experience.
3. Labor Market Dynamics
-
Addressing Labor Shortages: The auto industry, like many other manufacturing sectors, faces labor shortages, particularly for skilled and repetitive tasks. Humanoid robots can fill these gaps, ensuring continuity and efficiency in production.
-
Enhancing Worker Safety: By taking over hazardous and physically demanding tasks, humanoid robots can enhance worker safety and reduce workplace injuries.
Challenges to Adoption
1. High Initial Costs
- The high cost of acquiring and implementing humanoid robots can be a significant barrier, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises. However, as technology advances and economies of scale are realized, these costs are expected to decrease.
2. Technical Complexity
- The integration of humanoid robots into existing systems requires technical expertise and can be complex. Companies need to invest in training and infrastructure to support the adoption of these robots.
3. Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
- The deployment of humanoid robots must comply with regulatory standards and address ethical concerns, particularly regarding data privacy, job displacement, and safety. Developing a comprehensive regulatory framework is crucial for ensuring responsible adoption.
Adoption in other industries
Humanoid robots are poised to transform a variety of industries beyond the automotive sector. Their versatility, coupled with advances in artificial intelligence and robotics, makes them suitable for numerous applications.
Humanoid Robots: Industry Adoption Indicators
| Sector | Adoption Readiness | Technological Maturity | Economic Impact | Social Acceptance | Regulatory Environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | High | High | High | High | Moderate |
| Education | Moderate | Moderate | High | High | Moderate |
| Retail | High | Moderate | High | High | Low |
| Security | High | High | High | High | Moderate |
| Manufacturing | Very High | Very High | Very High | High | Moderate |
| Entertainment | High | Moderate | Moderate | High | Low |
| Home Assistance | Moderate | Moderate | High | Moderate | Low |
| Agriculture | Moderate | Moderate | High | High | Low |
| Construction | High | High | High | Moderate | Moderate |
Humanoid robots are set to revolutionize numerous industries by providing enhanced capabilities, improving efficiency, and addressing labor shortages. As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, the adoption of humanoid robots will likely accelerate, leading to transformative changes across various sectors. The future promises a closer integration of humanoid robots into everyday life, enhancing productivity, and improving quality of life in ways we are just beginning to imagine.
Here are several industries where we are likely to see significant adoption of humanoid robots:
1. Healthcare
Patient Care and Assistance
- Elderly Care: Humanoid robots can assist with daily activities, provide companionship, and monitor health parameters for the elderly, enabling them to live independently longer.
- Rehabilitation: Robots can assist patients with physical therapy by providing consistent and precise support during exercises, monitoring progress, and adjusting treatment plans based on real-time data.
Surgical Assistance
- Precision Surgery: Humanoid robots can assist surgeons in performing delicate and complex procedures, offering enhanced precision and reducing the risk of human error.
- Telemedicine: Robots can enable remote consultations and even remote surgeries, allowing access to healthcare services in underserved areas.
2. Education
Teaching Assistants
- Interactive Learning: Humanoid robots can engage students in interactive lessons, provide personalized tutoring, and assist teachers by handling routine tasks, allowing educators to focus on more complex instructional activities.
- Special Education: Robots can provide tailored educational experiences for students with special needs, offering consistent support and adapting to individual learning styles.
Research and Development
- Educational Tools: Humanoid robots can be used as tools in STEM education, helping students learn programming, robotics, and artificial intelligence through hands-on experience.
3. Retail and Hospitality
Customer Service
- Retail Assistants: Robots can help customers find products, provide information, and handle transactions, enhancing the shopping experience and freeing up human staff for more complex tasks.
- Concierge Services: In hotels and other hospitality settings, humanoid robots can provide concierge services, assist with check-ins, offer local information, and ensure a personalized guest experience.
Inventory Management
- Stock Monitoring: Robots can continuously monitor inventory levels, track product locations, and assist in restocking shelves, improving inventory accuracy and efficiency.
4. Security and Surveillance
Patrolling and Monitoring
- Public Safety: Humanoid robots can patrol public spaces, monitor for unusual activities, and provide real-time alerts to security personnel, enhancing safety and security in public areas.
- Event Security: Robots can assist in crowd management and provide security at large events, using advanced sensors to detect potential threats.
Disaster Response
- Emergency Assistance: In disaster scenarios, humanoid robots can assist in search and rescue operations, navigate hazardous environments, and provide immediate aid to victims.
5. Manufacturing and Warehousing
Flexible Automation
- Production Line Assistance: In manufacturing, humanoid robots can perform a variety of tasks, from assembly and welding to quality control, working alongside human workers or independently.
- Warehouse Operations: Robots can handle sorting, picking, packing, and transporting goods within warehouses, optimizing logistics and improving efficiency.
6. Entertainment and Media
Performance and Interaction
- Theme Parks and Museums: Humanoid robots can serve as guides, entertainers, and interactive exhibits in theme parks and museums, enhancing visitor engagement and experience.
- Film and Television: Robots can be used in production, providing new possibilities for special effects and live-action performances.
7. Home Assistance
Domestic Help
- Household Tasks: Humanoid robots can assist with cleaning, cooking, and other household chores, making daily life easier and more convenient.
- Child and Pet Care: Robots can monitor and interact with children and pets, providing companionship and ensuring safety.
8. Agriculture
Field Work
- Crop Monitoring: Robots can monitor crop health, apply pesticides, and manage irrigation systems, improving agricultural efficiency and sustainability.
- Harvesting: Humanoid robots can assist in the harvesting process, handling delicate crops with precision and reducing labor costs.
9. Construction
On-Site Assistance
- Building and Maintenance: Robots can assist with construction tasks, from bricklaying to painting, and perform maintenance activities, enhancing productivity and safety on construction sites.
Adoption Rates and Future Prospects
The adoption rate of humanoid robots varies across different sectors and regions. In industries such as manufacturing and logistics, where robots can significantly enhance efficiency and reduce costs, adoption rates are relatively high. However, in sectors like healthcare and customer service, adoption is slower due to higher costs and the complexity of integrating robots into human-centric environments.
1. Current Adoption Trends
-
Asia: Countries like Japan and South Korea are leading in the adoption of humanoid robots, driven by factors such as labor shortages, aging populations, and technological innovation. Robots are increasingly used in healthcare, manufacturing, and customer service.
-
Europe: Europe is also making significant strides, particularly in manufacturing and research. The European Union’s focus on Industry 4.0 and digital transformation has accelerated the adoption of robotics.
-
North America: In North America, the adoption of humanoid robots is growing in sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, and education. Companies like Boston Dynamics and Tesla are at the forefront of robotic innovation.
2. Future Prospects
The future of humanoid robots is promising, with several trends likely to drive their adoption:
-
Technological Advancements: Continued advancements in AI, machine learning, and materials science will enhance the capabilities and reduce the costs of humanoid robots.
-
Integration with Other Technologies: The integration of humanoid robots with other emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G, will open new possibilities for automation and connectivity.
-
Focus on Human-Centric Design: Designing robots that can better interact with humans and adapt to various environments will be crucial for their acceptance and effectiveness.
-
Regulatory Developments: The establishment of comprehensive regulatory frameworks will provide clarity and confidence for businesses and consumers, facilitating wider adoption.
Likely Adoption Rate of Humanoid Robots
| Sector | Current Human Labor Cost | Cost of Humanoid Robots | Adoption Rate (Low, Moderate, High) | Factors Influencing Adoption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | High | Moderate to Low | High | Cost savings, labor shortages, and need for consistent care |
| Education | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Personalized tutoring, administrative efficiency |
| Retail | Moderate | Low | High | Customer service, inventory management |
| Security | High | Moderate | High | Patrolling, monitoring, and hazard response |
| Manufacturing | High | Low | Very High | Assembly line automation, quality control |
| Entertainment | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Interactive experiences, engagement |
| Home Assistance | High | Moderate | High | Elderly care, household tasks |
| Agriculture | High | Low | High | Crop monitoring, harvesting |
| Construction | High | Moderate | Moderate to High | On-site assistance, maintenance |
Humanoid robot adoption rate model:
$$k(C,T,D,R,S)=α _1 C+α_2 T+α_3 D+α_4 R+α_5 S$$Primary coeeficients:
- Cost Ratio (C)
- Technological Maturity (T)
- Sector Demand (D)
- Regulatory Environment (R)
- Social Acceptance (S)
Essentially within 5 years of commercial availability of humanoid robots, the adoption rate is expected to be almost 100% in sectors such as healthcare, retail, and manufacturing, where the benefits of automation and efficiency are most pronounced. Supply is likely to be the primary moderating influence to this adoption rate, as the demand for humanoid robots is expected to outstrip supply in the initial years.
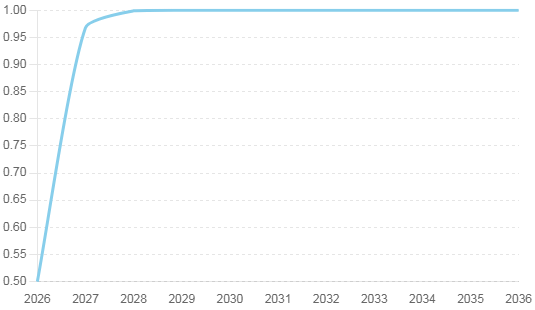
Sectors like education and entertainment are likely to see moderate (slower) adoption, driven by the need for interactive experiences and personalized services. As costs decrease and capabilities increase, the adoption rate of humanoid robots is expected to rise across various industries, transforming the way we work, learn, and interact with technology.